Cracking Wpa2 Wep Wifi Aircrack 10 Seconds Guide For Mac
Introduction With the popularity of wireless networks and mobile computing, an overall understanding of common security issues has become not only relevant, but very necessary for both home/SOHO users and IT professionals alike. This article is aimed at illustrating current security flaws in /WPA/WPA2.
Successfully cracking a wireless network assumes some basic familiarity with networking principles and terminology, as well as working with command-line tools. A basic familiarity with Linux can be helpful as well.
Disclaimer: Attempting to access a network other than your own, or one you have permission to use is illegal insome U.S. Speed Guide, Inc. Are not to be held liable for any damages resulting from the use or misuse of the information in this article. To successfully crack /WPA, you first need to be able to set your wireless network card in 'monitor' mode to passively capture packets without being associated with a network. This mode is driver-dependent, and only a relatively small number of network cards support this mode under Windows. One of the best free utilities for monitoring wireless traffic and cracking WEP/WPA-PSK keys is the suite, which we will use throughout this article. It has both Linux and Windows versions (provided your network card is supported under Windows).
The aircrack-ng site has a comprehensive list of supported network cards available here:. If your network card is not supported under Windows, one can use a free Linux Live CD to boot the system. Is probably the most commonly used distribution, since it runs from a Live CD, and has aircrack-ng and a number of related security auduting tools already installed.
For this article, I am using aircrack-ng on another Linux distro (Fedora Core) on a Sony Vaio SZ-680 laptop, using the built-in Intel 4965agn network card. If you're using the BackTrack CD aircrack-ng is already installed, with my version of linux it was as simple as finding it with: yum search aircrack-ng yum install aircrack-ng The aircrack-ng suite is a collection of command-line programs aimed at and WPA-PSK key cracking. The ones we will be using are: airmon-ng - script used for switching the wireless network card to monitor mode airodump-ng - for monitoring and capturing network packets aireplay-ng - used to generate additional traffic on the wireless network aircrack-ng - used to recover the key, or launch a dictionary attack on WPA-PSK using the captured data. Setup (airmon-ng) As mentioned above, to capture network traffic wihtout being associated with an, we need to set the wireless network card in monitor mode. To do that under linux, in a terminal window (logged in as root), type: iwconfig (to find all wireless network interfaces and their status) airmon-ng start wlan0 (to set in monitor mode, you may have to substitute wlan0 for your own interface name) Note: You can use the su command to switch to a root account.
Other related Linux commands: ifconfig (to list available network interfaces, my network card is listed as wlan0) ifconfig wlan0 down (to stop the specified network card) ifconfig wlan0 hw ether 00:11:22:33:44:55 (change the address of a - can even simulate the of an associated client. Should be stopped before chaning address) iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor (to set the network card in monitor mode) ifconfig wlan0 up (to start the network card) iwconfig - similar to ifconfig, but dedicated to the wireless interfaces. Recon Stage (airodump-ng) This step assumes you've already set your wireless network interface in monitor mode. It can be checked by executing the iwconfig command. Next step is finding available wireless networks, and choosing your target: airodump-ng mon0 - monitors all channels, listing available access points and associated clients within range. It is best to select a target network with strong signal (PWR column), more traffic (Beacons/Data columns) and associated clients (listed below all access points). Once you've selected a target, note its Channel and BSSID ( address).
Also note any STATION associated with the same BSSID (client addresses). Running airodump-ng displays all wireless access points and associated clients in range, as well as addresses, signal levels and other information about them. Is much easier to crack than WPA-PSK, as it only requires data capturing (between 20k and 40k packets), while WPA-PSK needs a dictionary attack on a captured handshake between the and an associated client which may or may not work. Capture Data (airodump-ng) To capture data into a file, we use the airodump-ng tool again, with some additional switches to target a specific AP and channel.
Most importantly, you should restrict monitoring to a single channel to speed up data collection, otherwise the wireless card has to alternate between all channels. Assuming our wireless card is mon0, and we want to capture packets on channel 6 into a text file called data: airodump-ng -c 6 bssid 00:0F:CC:7D:5A:74 -w data mon0 (-c6 switch would capture data on channel 6, bssid 00:0F:CC:7D:5A:74 is the address of our target, -w data specifies that we want to save captured packets into a file called 'data' in the current directory, mon0 is our wireless network adapter) Running airodump-ng on a single channel targeting a specific Notes: You typically need between 20,000 and 40,000 data packets to successfully recover a key. One can also use the '-ivs' switch with the airodump-ng command to capture only IVs, instead of whole packets, reducing the required disk space.
However, this switch can only be used if targeting a network, and renders some types of attacks useless. Increase Traffic (aireplay-ng) - optional step for cracking An active network can usually be penetrated within a few minutes. However, slow networks can take hours, even days to collect enough data for recovering the key. This optional step allows a compatible network interface to inject/generate packets to increase traffic on the wireless network, therefore greatly reducing the time required for capturing data. The aireplay-ng command should be executed in a separate terminal window, concurrent to airodump-ng. It requires a compatible network card and driver that allows for injection mode.
Assuming your network card is capable of injecting packets, in a separate terminal window try: aireplay-ng -3 -b 00:0F:CC:7D:5A:74 -h 00:14:A5:2F:A7:DE -x 50 wlan0 -3 - this specifies the type of attack, in our case ARP-request replay -b. address of -h. address of associated client from airodump -x 50 - limit to sending 50 packets per second wlan0 - our wireless network interface aireplay-ng allows for injecting packets to greatly reduce the time required to recover a key Notes: To test whether your is able to inject packets, you may want to try: aireplay-ng -9 wlan0.
You may also want to read the information available. To see all available replay attacks, type just: aireplay-ng 5. Crack (aircrack-ng) cracking is a simple process, only requiring collection of enough data to then extract the key and connect to the network.
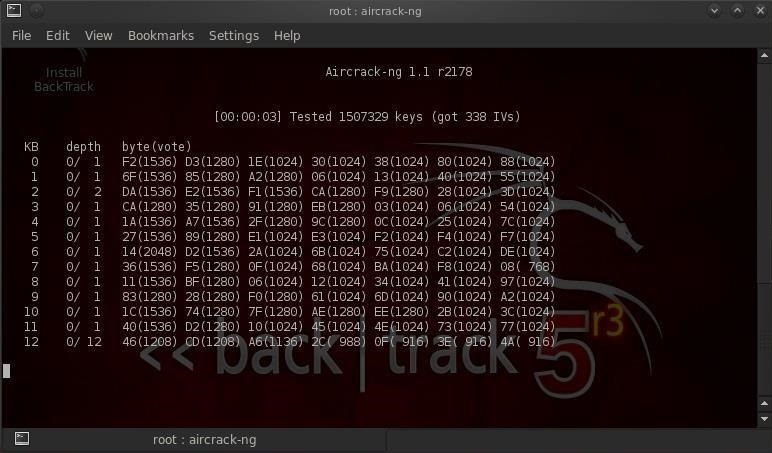
You can crack the key while capturing data. In fact, aircrack-ng will re-attempt cracking the key after every 5000 packets. To attempt recovering the key, in a new terminal window, type: aircrack-ng data.cap (assuming your capture file is called data.cap, and is located in the same directory) aircrack-ng can successfully recover a key with 10-40k captured packets.
The retreived key is in hexadecimal, and can be entered directly into a wireless client omitting the ':' separators Notes: If your data file contains ivs/packets from different access points, you may be presented with a list to choose which one to recover. Usually, between 20k and 40k packets are needed to successfully crack a key. It may sometimes work with as few as 10,000 packets with short keys. Crack WPA or PSK (aircrack-ng) WPA, unlike rotates the network key on a per- basis, rendering the method of penetration useless.
Cracking a WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK key requires a dictionary attack on a handshake between an and a client. What this means is, you need to wait until a wireless client associates with the network (or deassociate an already connected client so they automatically reconnect). All that needs to be captured is the initial 'four-way-handshake' association between the and a client. Essentially, the weakness of WPA-PSK comes down to the passphrase. A short/weak passphrase makes it vulnerable to dictionary attacks. To successfully crack a WPA-PSK network, you first need a capture file containing handshake data.
This can be obtained using the same technique as with in step 3 above, using airodump-ng. You may also try to deauthenticate an associated client to speed up this process of capturing a handshake, using: aireplay-ng -deauth 3 -a MACAP -c MACClient mon0 (where MACIP is the address of the, MACClient is the address of an associated client, mon0 is your wireless ).
The command output looks something like: 12:34:56 Waiting for beakon frame (BSSID: 00:11:22:33:44:55:66) on channel 6 12:34:56 Sending 64 directed DeAuth. STMAC: 00:11:22:33:44:55:66 5:62 ACKs Note the last two numbers in brackets 5:62 ACKs show the number of acknowledgements received from the client (first number) and the AP (second number). It is important to have some number greater than zero in both. If the first number is zero, that indicates that you're too far from the associated client to be able to send deauth packets to it, you may want to try adding a reflector to your antenna (even a simple manilla folder with aluminum foil stapled to it works as a reflector to increase range and concentrate the signal significantly), or use a larger antenna. Simple antenna reflector using aluminum foil stapled to a manilla folder can concentrate the signal and increase range significantly.
For best results, you'll have to place the antenna exactly in the middle and change direction as necessary. Of course there are better reflectors out there, a parabolic reflector would offer even higher gain, for example.
Once you have captured a four-way handshake, you also need a large/relevant dictinary file (commonly known as wordlists) with common passphrases. See related links below for some wordlist links. You can, then execute the following command in a linux terminal window (assuming both the dictionary file and captured data file are in the same directory): aircrack-ng -w wordlist capturefile (where wordlist is your dictionary file, and capturefile is a.cap file with a valid handshake) Additional Notes: Cracking WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK only needs 4 packets of data from the network (a handshake).
After that, an offline dictionary attack on that handshake takes much longer, and will only succeed with weak passphrases and good dictionary files. A good size wordlist should be 20+ Megabytes in size, cracking a strong passphrase will take hours and is CPU intensive. Cracking /WPA2 usually takes many hours, testing tens of millions of possible keys for the chance to stumble on a combination of common numerals or dictionary words. Still, a weak/short/common/human-readable passphrase can be broken within a few minutes using an offline dictionary attack. My record time was less than a minute on an all-caps 10-character passphrase using common words with less than 11,000 tested keys! A modern laptop can process over 10 Million possible keys in less than 3 hours.
Hashes the network key using the wireless 's as salt. This prevents the statistical key-grabbing techniques that broke, and makes hash precomputation more dificult because the specific needs to be added as salt for the hash.
There are some tools like coWPAtty that can use precomputed hash files to speed up dictionary attacks. Those hash files can be very effective (sicne they're much less CPU intensive and therefore faster), but quite big in size. The has computed hash tables for the 1000 most common against a million common passphrases that are 7Gb and 33Gb in size. Crack using the Vulnerability (Reaver) Many devices are aslo vulnerable to a WPS ( Protected Setup) vulnerability described in US-CERT TA12-006A Alert. Provides simplified mechanisms to secure wireless networks, most often using a PIN as a shared secret to authenticate clients and share the /WPA/WPA2 passwords and keys. The external PIN exchange mechanism is susceptible to brute-force attacks that allow for bypassing wireless security in a relatively short time (few hours). The only remedy is to turn off, or use an updated that specifically addresses this issue. A free Linux open-source tool called Reaver is able to exploit the vulnerability. To launch an attack: 1.
Install Reaver - 2. Set your network adapter in monitor mode as described above, using: ifconfig wlan0 down iwconfig wlan0 mode monitor ifconfig wlan0 up Alternatively, you can put your network card in monitor mode using: airmon-ng start wlan0 (this will produce an alternate adapter name for the virtual monitor mode adapter, usually mon0 ) 3.
Before using Reaver to initiate a brute-force attack, you may want to check which access points in the area have enabled and are vulnerable to the attack. You can identify them using the 'wash' Reaver command as follows: wash -i mon0 -ignore-fcs 4. Run Reaver (it only requires two inputs: the interface to use, and the address of the target) reaver -i mon0 -b 00:01:02:03:04:05 -vv There are a number of other parameters that one can explore to further tweak the attack that are usually not required, such as changing the delay between PIN attempts, setting the tool to pause when the stops responding, responding to the to clear out failed attempts, etc. The above example adds '-vv' to turn on full verbose mode, you can use '-v' instead for fewer messages. Reaver has a number of other switches (check with -help), for example ' -c11' will manually set it to use only channel 11, ' -no-nacks' may help with some APs. Spoof client address if needed.
In some cases you may want/need to spoof your address. Reaver supports spoofing with the - option, however, for it to work you will have to change the address of your card's physical interface (wlan0) first, before you specify the reaver option to the virtual monitor interface (usually mon0).
To spoof the address: ifconfig wlan0 down ifconfig wlan0 hw ether 00:11:22:33:44:55 ifconfig wlan0 up airmon-ng start wlan0 reaver -i mon0 -b.vv -mac=00:11:22:33:44:55 An attack using Reaver typically takes between 4 and 8 hours (provided requests are not being limited by the AP), and returns the, WPS PIN and passphrase for the target network. Note that some routers may lock you out for a few minutes if they detect excessive failed PIN attempts, in such cases it may take over 24 hours. Notes: Some routers (including most popular Cisco/Linksys models) will NOT turn off even if turned off via the radio button in their web admin interface. You may be able to turn it off using third-party, such as DD-WRT (wich does not support ). Reportedly, some models/vendors/ISPs all come configured with a default pin. Common pins are 12345670, 00005678, 01230000, etc.
Buy cocoa para mac os x cocoa for mac. If you own a Mac running Mac OS X, you already have Cocoa, and all the. To get the most out of this text, you will need to be running Mac OS X 10.3 or later. Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface (API) for their. Rhapsody evolved into Mac OS X, and the Yellow Box became Cocoa. Paragraph layout can be controlled automatically or by the user, using a. Programming Mac OS X with Cocoa for Beginners 2nd Edition/What Is Cocoa? Cocoa is what Apple itself uses to develop Mac apps that come with Mac OS X such as Finder. You can look around inside of the System Folder and get an idea of what's there, but. Create a collection Download as PDF Printable version. Cocoa Programming for Mac OS X and millions of other books are available for Amazon. Get your Kindle here, or download a FREE Kindle Reading App.
Reaver attempts known default pins first. Reaver comilation requires libpcap (pcap-devel) and sq3-devel (sqlite3-dev) installed, or you will get a 'pcap library not found' error. Troubleshooting Tips Even with the above tools properly installed, it is common to get a few errors/warnings during the attacks, usually related to timeouts, poor signal, or interface driver not supporting monitor/injection modes. Here are some points to consider: 1. Is your adapter properly set in monitor mode?
Does the adapter driver support injection (is aireplay-ng working)? Do you have to spoof your address (if AP limits MACs, change both physical and virtual monitor interface)? Do you have a good signal to the AP? Do you see associated clients (for handshake capture)? Do you see pin count incrementing (Reaver cracking)? Does the target AP support and is it enabled (for attacks, check with the 'wash' command)?
Final Thoughts As demonstrated above, cracking has become increasingly easier over the years, and what used to take hundreds of thousands packets and days of capturing data can be accomplished today within 15 minutes with a mere 20k data frames. Simply put, cracking is trivial. /WPA2-PSK is holding its ground if using a strong, long key.
Cracking Wpa2 Wep Wifi Aircrack 10 Seconds Guide For Mac Download
However, weak passphrases are vulnerable to dictionary attacks. WPA/WPA2 may be on borrowed time as well, according to some. The vulnerability renders even /WPA2 secured wireless networks very vulnerable. An extensive list of vulnerable devices is available here:. Note that some routers (including most popular Cisco/Linksys models) will NOT turn off even if turned off via the radio button in their web admin interface. You may be able to turn it off using third-party, such as DD-WRT (which does not support ).
Related Links - Torrent search - wordlists. Specter: The security of your local wireless network is an important concept. Understanding how it can be hacked helps make more educated decisions about protecting it. Hacking a wireless network can expose the local computers and all shared information to an attacker, or, more commonly outsiders can use your wireless lan to connect to the internet without your knowledge. Hypothetically, imagine a neighbor's kid hacks into your Wireless LAN and uses P2P to download illegal files or spread viruses.
There is a potential you can be held accountable for the information that passes through your equipment. All channels are equally vulnerable to an attack, what makes a difference is the type of security/encryption used and the length of the key. If you want hacking tips, while there are some here that may help you, stop asking here if you are that lacking in creativity/sense/originality.
This was meant as a guide to EDUCATE PEOPLE TO THE PROBLEMS WITH USING WIFI. Seriously, do you think ANY network is secure? And yes, that includes wired networks. THERE IS ALWAYS SOMETHING THAT WILL ALLOW YOU SOME SORT OF ACCESS. People, get a grip on your own lack of intelligence or skill, and THINK ABOUT WHAT YOU ARE TRYING TO DO. Then post to the appropriate places to get your desired response. Seriously, I thought people were getting smarter.
In previous tutorial,i have explained you the how to put the android smartphone into monitor mode,by continuing the previous tutorial in this tutorial,i will show you how to hack wifi with android smartphone after enabling the monitor mode on android.In this tutorial,i am using bcmon and reaver application to hack wifi on android. How To Hack WiFi With Android? Wifi Password hacking for android require following:. Android smartphone must be rooted. Bcmon apk is installed-This tool enables Monitor Mode on your rooted device with Broadcom chipset, which is must for wifi password hack via android. RfA Reaver for Android - A WiFi penetration tool to crack WPS, WPA and WPA2-psk key. First install bcmon and reaver application into android smartphone.
Launch bcmon application and run for 5-10 seconds. Now make the changes as shown in to put the android smartphone into monitor mode. Then Click on ' enable monitor mode' button. It's time to execute the reaver application Reaver. Then scan for available wifi access point.
Select the target wifi network which you want to hack.Don't forget to enable Monitor Mode and Make sure that the ' Automatic advanced settings' checkbox is checked. Monitor-Mode.
After selecting the network to hack and hit ' Start Attack'. It will take upto 6 hours to hack depending upon the length of key and encryption And sometimes it may failed to hack the target wireless network. Start-attack How To Hack WEP Protected Wifi Using Android Terminal. Download and run bcmon application.
Now ' Run terminal' application in android smartphone. Now type airodump-ng ath0 in terminal and tap the Enter button. Here select the target wireless network and Note down the mac address and channel no which further required to hack wep protected wifi. airodump-ng -c 9 -bssid 00:14:6C:7E:40:80 -w outputfile ath0 airodump-ng. Note:- c 9: broadcasting channel,-bssid: Mac Address of the router, -w is for output file name. Stop scanning after collecting packet between 0 packets.
After collecting the enough packet,crack the wifi password using aircrack-ng command in terminal.type aircrack-ng outputfile.cap and tap Enter. This command will crack the password from scanned packets aircrack-ng.